Problem
Longest Increasing Subsequence(LIS) 문제는 주어진 배열의 subsequence들 중에서 오름차순으로 정렬되었으며, 그 중에서도 길이가 가장 긴 subsequence를 찾아내는 문제이다.
What is subsequence?
배열 {1, 2, 3}의 subsequence는 {1}, {2}, {3}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {1, 2, 3} 이다.
이 배열의 LIS를 굳이 따지자면, {1, 2, 3}이 된다.
Example
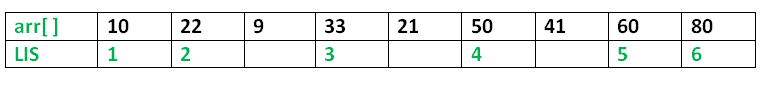
위와 같은 배열이 주어졌을 때, LIS는 {10, 22, 33, 50, 60, 80}이 되고, 그 길이는 6이 된다.
Input: arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 1, 20}
Output: Length of LIS = 3
The longest increasing subsequence is 3, 10, 20
Input: arr[] = {3, 2}
Output: Length of LIS = 1
The longest increasing subsequences are {3} and {2}
Input: arr[] = {50, 3, 10, 7, 40, 80}
Output: Length of LIS = 4
The longest increasing subsequence is {3, 7, 40, 80}Recursive Solution
Optimal Substructure
배열 arr[0, .. , n-1]이 주어졌을 때, L(i)라는 함수를 통해 arr[i]가 LIS의 마지막 요소인 경우의 LIS 길이를 구하고자 한다.
그러면 L(i)는 재귀적으로 다음과 같이 활용될 수 있다.
L(i) = 1 + max( L(j) ) //where 0 < j < i and arr[j] < arr[i];
or
L(i) = 1 //if no such j exists.주어진 배열의 LIS를 찾기 위해서, 0<i<n의 조건 중에서 max(L(i))를 리턴해야 한다.
공식적으로 arr[j] < arr[i] (j <ㅠ i)인 경우에, index i에서 LIS의 길이는 i보다 앞에서 끝나는 모든 LIS의 최대 길이보다 1만큼 더 크다.
그러므로 이 문제는 Dynamic Programming의 Optimal Substructure 특성에 해당한다고 말할 수 있으니, 전체 문제에 대한 하위 문제들을 해결해나가는 방식으로 문제를 풀 수 있다.
접근 방식을 보다 명확히 그리면 다음과 같다.
Input : arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 11}
f(i): index i에서 끝나는 모든 subsequence의 LIS를 나타냄
(LIS(1)=1)
f(4) {f(4) = 1 + max(f(1), f(2), f(3))}
/ | \
f(1) f(2) f(3) {f(3) = 1, f(2) and f(1) are > f(3)}
| | \
f(1) f(2) f(1) {f(2) = 1 + max(f(1)}
|
f(1) {f(1) = 1}Java 구현
class LIS {
//LIS 저장 용도
static int max_ref;
/*
재귀 함수 호출을 위해서 함수는 2가지를 리턴해야 한다.
1) arr[n-1]에서 끝나는 LIS의 길이
이를 위해 max_ending_here라는 변수 사용
2) arr[n-1] 이전에 전체적인 LIS의 최대 길이
이를 위해 max_ref라는 변수 사용
*/
static int _lis(int arr[], int n) {
//base case
if (n == 1) return 1;
/*
재귀적으로 arr[0], ... , arr[n-2]에서 끝나는 LIS들을 찾는다.
max_ending_here와 arr[n-1]은 갱신되어야 한다.
*/
int res, max_ending_here = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res = _lis(arr, i);
if (arr[i - 1] < arr[n - 1]
&& res + 1 > max_ending_here) {
max_ending_here = res + 1;
}
}
/*
max_ending_here와 전체 max 값을 비교 후,
max_ending_here 값이 더 크다면 전체 max 값에 대입
*/
if (max_ref < max_ending_here) {
max_ref = max_ending_here;
}
//arr[n-1]에서 끝나는 LIS의 길이를 리턴
return max_ending_here;
}
//The wrapper function for _lis()
static int lis(int arr[], int n) {
max_ref = 1;
_lis(arr, n);
return max_ref;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n) + "\n");
}
}Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : 하위 문제들이 중복되기 때문에 기하급수적이다.
- Auxiliary Space : O(1). 내부 스택 공간 이외에는 별도의 공간을 필요로 하지 않는다.
Dynamic Programming Solution
여타 DP 문제들과 마찬가지로, 이 문제 또한 Memoization 이나 Tabulation 기법을 통해서 시간복잡도 문제를 완화할 수 있다.
Iteration-wise simulation
Input : arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 11}
LIS[] = {1, 1, 1, 1} (initially)- arr[2] > arr[1] {LIS[2] = max(LIS [2], LIS[1]+1)=2}
- arr[3] < arr[1] {No change}
- arr[3] < arr[2] {No change}
- arr[4] > arr[1] {LIS[4] = max(LIS [4], LIS[1]+1)=2}
- arr[4] > arr[2] {LIS[4] = max(LIS [4], LIS[2]+1)=3}
- arr[4] > arr[3] {LIS[4] = max(LIS [4], LIS[3]+1)=3}
이처럼, Tabulation 기법을 활용해서 중복되는 하위 문제들에 대한 중복 계산 문제를 피할 수 있다.
Java 구현
class LIS {
static int lis(int[] arr, int n) {
int lis[] = new int[n];
int i, j, max = 0;
//모든 인덱스들에 LIS 초기값 1 대입
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) lis[i] = 1;
//bottom up 방식으로 하위 문제들 해결
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1) {
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
}
}
}
//저장된 값들 중 최대값 pick
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (max < lis[i]) max = lis[i];
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n) + "\n")
}
}Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : O(n²). 이중 반복문이 사용된다.
- Auxiliary Space : O(n). LIS를 저장하기 위한 배열이 사용된다.
More Comment
LIS 문제를 O(N log N)의 시간복잡도로 해결할 수 있다고도 한다.
하지만 솔직히, O(n²)의 방식도 지금 내 수준에서는 이해가 잘 되지 않으므로, O(N log N) 방식의 포스팅은 뒤로 미루려 한다.
아래 쪽에 링크를 남겨두고 나중에 꼭 공부해야겠다.
현재 필자는 DP에 대해 공부하고 있으며, DP의 관련 문제들을 이해하는 데에 더 초점을 두고 있다.
References
'Algorithm > 꼭 기억해둘 유명 Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 0-1 Knapsack Problem | Dynamic Programming (0) | 2021.09.22 |
|---|---|
| Ugly Numbers (0) | 2021.09.20 |
| Coin Change | Dynamic Programming (0) | 2021.09.19 |
| Sudoku | Backtracking (0) | 2021.09.18 |